Erectile Dysfunction and Impotence
What Is Impotence?
Impotence, or Erectile Dysfunction, is the inability to obtain or maintain an erection, and:
-
Obtain an erection firm enough for satisfactory intercourse or
-
Maintain an erection long enough to have sexual intercourse to the satisfaction of both partners.
Many people believe that impotence and the end of sexual life is a normal part of aging. It is not. An estimated 30 million American men are affected by impotence. Despite the widespread nature of the condition, fewer than five percent of those affected will see a physician for treatment. Many men may feel uncomfortable discussing this topic with a physician, family or friends.
The majority of men suffering from impotence have a significant underlying medical problem causing their erectile difficulties. About 95 percent of all impotence cases can be successfully treated.
What Causes Impotence?
A variety of factors can cause impotence including:
-
A hormonal imbalance or not having enough testosterone in the blood can cause impotence.
-
A psychological disturbance can cause impotence. Since the brain is needed in the process of obtaining an erection, the brain may be subconsciously inhibiting erections.
-
Damaged or diseased nerves can cause impotence. In order to obtain an erection, the brain and spinal cord send signals to the penis through nerves. Nerves can be damaged by pelvic surgery, trauma from an accident, or radiation treatment. Diseases which affect the nerves include: Diabetes, Multiple Sclerosis, Parkinson's Disease and Alzheimer's Disease.
-
Poor blood supply to the penis can cause impotence. Since an erection happens when blood becomes trapped in the penis, diseases of the blood vessels can lead to impotence. Diseases such as: Diabetes, Coronary Disease, High Blood Pressure, Heart Disease and Peripheral Vascular Disease, are the most common.
-
Failure to trap blood within the penis can cause impotence. This happens when blood enters the penis, but leaves just as quickly not allowing the penis to fill with blood.
-
Various medications can lead to impotence, such as medications commonly used to treat blood pressure, heart, and ulcers.
-
The excessive use of alcohol or tobacco can cause impotence.
It is important to remember that these causes of impotence are real medical diseases. They affect the body in many ways. Like any other disease, impotence needs to be diagnosed and treated. If the problem is recognized and treated properly, nearly every man who wants to can have erections and an active and full sex life.
What Will The Urologist Do?
The urologist may ask you specific questions about your erections and sexual practices. This will help determine the nature of the problem, and how severe it is. Your urologist will then examine you, including an examination of your penis and testicles, and perform a rectal examination of your prostate. These are necessary in helping to find the best way to treat your impotence.
The urologist may order blood tests to check the level of testosterone in your body. Additional tests may be necessary to measure pressures and blood flow inside the penis.
What Treatment Is Available?
Oral Medication
Many herbs and medications have been thought to enhance erections and sex drive. Viagra®, the first oral medication for the treatment of impotence, was recently approved by the FDA and introduced into the marketplace. The medication is taken orally when the patient is sexually stimulated, the drug causes the penile blood vessels to dilate resulting in an erection. Based on the limited information available at this time, Viagra® seems to be effective in most patients.
Injection Therapy
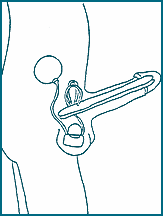
Injection therapy is the most commonly prescribed treatment for erectile problems. Injections can produce a natural and normal erection that cannot be distinguished from a naturally occurring erection. Devices that will inject the medicine for you, such as Caverject®, are available. You only need to place the syringe in the device, place the device against your penis and push a button. This can make the injection method even easier.
Hormone Therapy
If during your evaluation, you are found to have low levels of testosterone,
then testosterone replacement may restore normal erections.
Testosterone replacement may be given by injection or by skin patch. If your level is normal, more testosterone will not help.
Vacuum Erection Devices
Vacuum erection devices can produce artificial erections by creating a vacuum
that draws blood into the penis. Once the blood is in the penis, a special rubber
band is placed at the base of the penis, and the vacuum devise is removed.
This leaves the man with a penis engorged with blood and erect.
The band needs to be removed immediately at the end of intercourse.
Penile Implants
If no other form of therapy works, or does not give the desired effect,
then a device can be placed inside the erectile bodies of the penis.
There are two general types of devices, one which stays rigid all the time,
and one which inflates to become rigid, and deflates to become soft.
The inflatable device usually gives the best results and patient satisfaction.
Urethral Suppositories
A drug treatment, called MUSE®, uses a unique approach to treat erectile dysfunction. It is based on the discovery that the urethra, a tube in the penis that passes urine from the bladder to the outside of the body, can absorb certain medications into the surrounding erectile tissues to create an erection. The MUSE® system uses prostaglandin E1, the same medication used in self injection therapy, and has been approved by the FDA for treatment of impotence. An erection should begin within five to ten minutes after administering MUSE®. The effect lasts approximately 30 – 60 minutes. However, the actual duration will vary from patient to patient.
Experimental Therapy
At Southeastern Urological Center, P.A., we often participate with pharmaceutical and equipment companies to test new treatments for impotence. These new and experimental forms of therapy may be of benefit to you. If you are interested in participating in a research project, please advise your doctor.
If you would like more information about impotence, or would like to schedule an appointment at Southeastern Urological Center, P.A., please call (850) 309-0400, or toll free, (800) 689-6678.